Get Microsoft 365 Unified Audit Logs data
Microsoft 365 Unified Audit Logs are a centralized log of all activities performed within a Microsoft 365 tenant. These logs provide a detailed record of user, administrator and system activities, including information about when specific actions were performed, who performed them and from what location. The Unified Audit Logs help organizations to monitor and track changes to their Microsoft 365 environment, and assist with compliance, security, and troubleshooting efforts.
The logs can be used to track a wide range of activities, including:
- Changes to user accounts and settings
- Login activity, including successful and failed sign-ins
- Mailbox activity, such as email sends, receives and deletes
- SharePoint and OneDrive activity, including document and folder updates
- Exchange Online activity, including message tracking and changes to mailboxes
- Teams activity, including team and channel creation, updates, and deletions
- Power Platform activity, including flow and PowerApps creation and updates
- The Unified Audit Logs are stored in a central location, making it easy to access and search logs from multiple services in one place. They can be searched and filtered using a range of parameters, such as date range, user, IP address, and action type.
In conclusion, Microsoft 365 Unified Audit Logs provide a valuable tool for organizations to monitor and track changes to their Microsoft 365 environment, assist with compliance and security efforts, and provide a centralized location for security event information.
Enable and search for logs using the ExchangeOnline PowerShell
Open the PowerShell ISE as administrator and type:
Something to keep in mind that by default the Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet will return Exchange related logs.
You need to specify the RecordType to get SharePoint specific logs for example:
Here is the list with Record Types here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/audit-log-search?view=o365-worldwide#microsoft-365-services-that-support-auditing
Bear in mind SharePoint record type can be narrowed down to: SharePointFileOperation,SharePointSharingOperation, SharePointListOperation, SharePointCommentOperation.
Another handy feature of this cmdlet is the -Operations parameter allowing you to narrow down the search scope even more:
Having the option to specify the operations, is really handy as you don't have to query big logs set later.
A list with all operations is available here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/audit-log-activities?view=o365-worldwide
Search for SharePoint Online audit logs using PowerShell
This can be done by using PnP PowerShell. Open the PowerShell ISE as administrator and type:
Connect to the Microsoft 365 Management APIs using Azure AD app
You will need a Azure AD and a Client Id and Secret to connect to the APIs. So you will have to create a new Azure Ad App
- Register an App: To start working with the Microsoft 365 Management API, you will need to register an app in Azure Active Directory. This app will be used to authenticate and authorize your API calls.
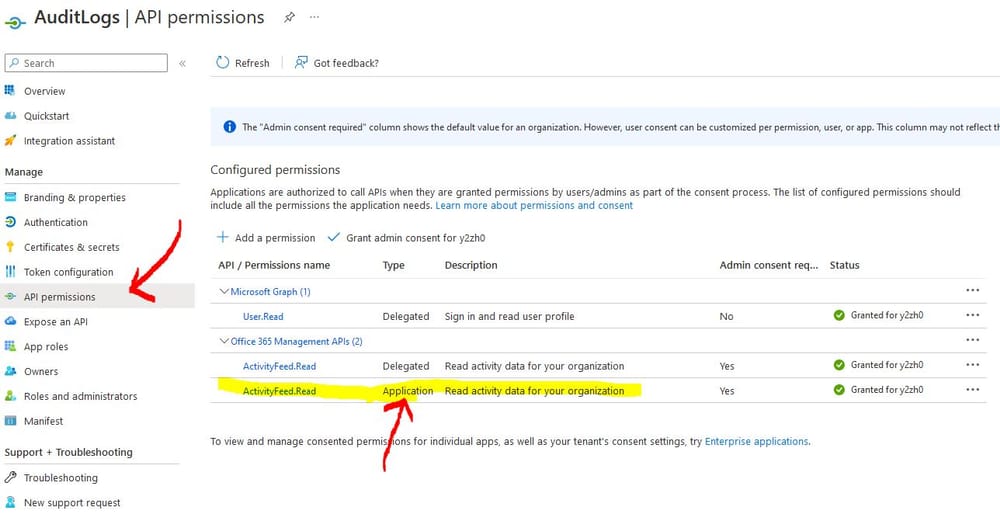
- Go to API Permissions and add Office 365 Management APIs -> Application -> ActivityFeed.Read permission
- Once you close the window find and click on the Grant admin consent button
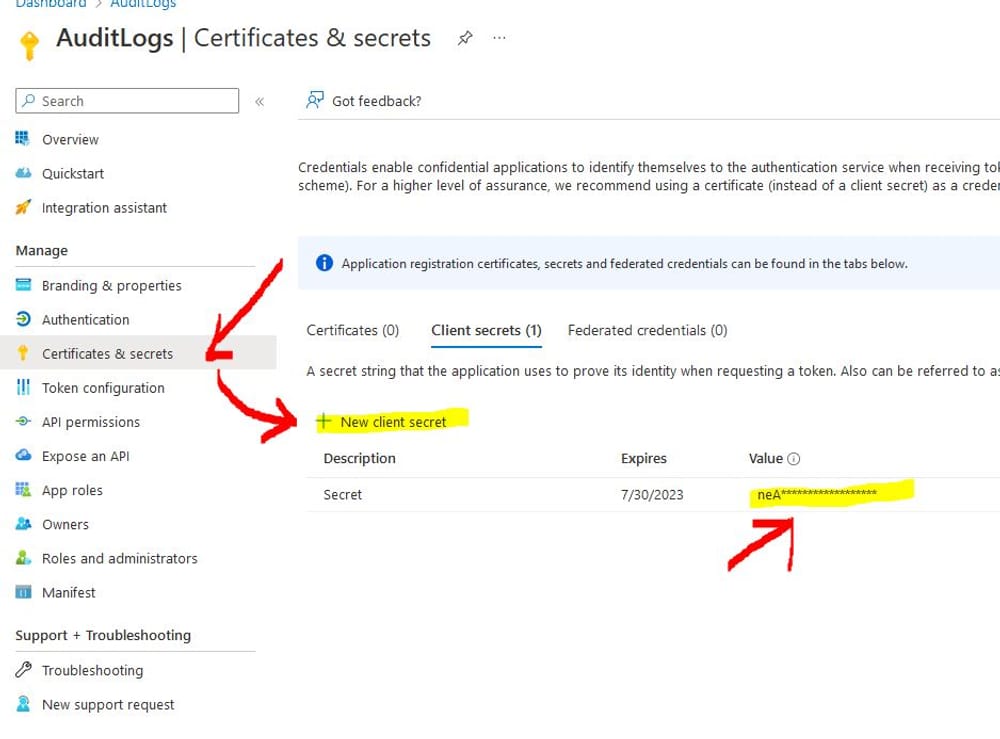
- Then go to the certificates and secrets and create a new client secret
- Copy the secret value so you can use it with powershell or rest api
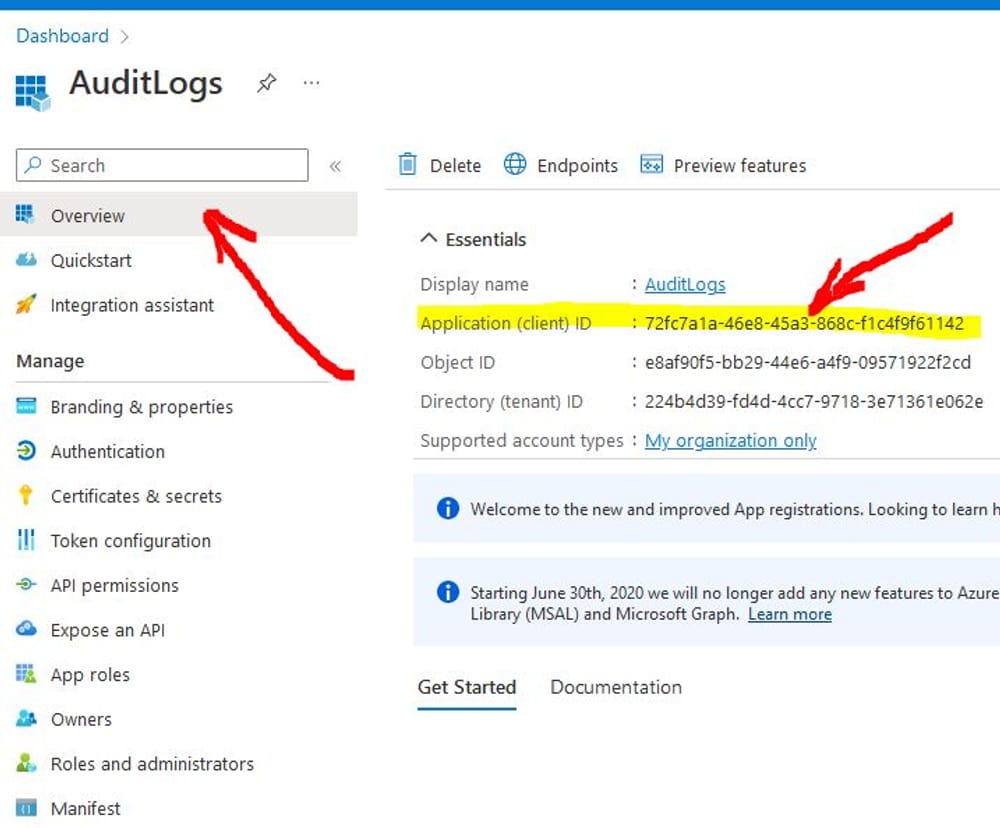
- Go to the Overview panel and copy the Client Id so you can use it with powershell or rest api
Search for unified audit logs by using the Rest API and your Azure AD app Client Id and Secret
- To start working with the Microsoft 365 Management API, you will need the registered app in Azure Active Directory. This app will be used to authenticate and authorize your API calls.
- Get an Access Token: Next, you will need to obtain an access token from Azure Active Directory. You can do this using the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials flow, where you provide your app’s client ID and secret to the Azure AD token endpoint. The token endpoint will then return an access token that you can use to make API calls.
- Make an API Call: Once you have obtained an access token, you can make an API call to the Microsoft 365 Management API. For example, to retrieve a list of all audit logs, you can make a GET request to the following endpoint: https://manage.office.com/api/v1.0/<tenant-id>/activity/feed/subscriptions/content.
- Handle the Response: The API will return a JSON response containing the data you requested. You can parse this response and use the data in your application as needed.
Here is an example of a code snippet in Python to get the list of audit logs in a Microsoft 365 tenant:
Python code
JavaScript Code
Microsoft 365 Management Audit REST APIs
Once you have access token, a GET request can be executed to identify the blob locations of the logs:
- PublisherIdentifier is the tenant ID.
- contentType:
- Audit.AzureActiveDirectory
- Audit.Exchange
- Audit.SharePoint
- Audit.General (includes all other workloads not included in the previous content types)
- DLP.All (DLP events only for all workloads)
startTime amd endTime: Optional datetimes (UTC) indicating the time range of content to return, based on when the content became available. The time range is inclusive with respect to startTime (startTime <= contentCreated) and exclusive with respect to endTime (contentCreated < endTime), so that non-overlapping, incrementing time intervals can used to page through available content.
YYYY-MM-DD
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS
Both must be specified (or both omitted) and they must be no more than 24 hours apart, with the start time no more than 7 days in the past. By default, if startTime and endTime are omitted, then the content available in the last 24 hours is returned.
NOTE: Even though it is possible to specify a startTime and endTime more than 24 hours apart, this is not recommended. Furthermore, if you do get any results in response to a request for more than 24 hours, these could be partial results and should not be taken into account. The request should be issued with an interval of no more than 24 hours between the startTime and endTime.
Once you have the blob logs locations you can execute GET requests to retrieve the data:
The Exchange Online cmdlet is using different api
Useful Links:
